How to operate a drone is a question many ask, and the answer encompasses far more than simply lifting off and landing. This guide delves into the intricacies of safe and responsible drone operation, from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers and ethical considerations. We’ll explore everything from mastering the controls and understanding flight modes to capturing stunning aerial photography and navigating the legal landscape.
Prepare to unlock the skies and embark on a journey of aerial exploration.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the process into manageable steps, covering everything from basic operation to advanced techniques. We’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to fly your drone safely and responsibly, capturing breathtaking images and videos along the way. Understanding the technology, the regulations, and the best practices is key, and we’ll cover all of that in detail.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring both safety and operational success. This involves a series of checks to identify potential problems and mitigate risks. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, or even injury.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should include the following steps:
- Battery Check: Verify the battery level is sufficient for the planned flight duration. Inspect the battery for any signs of damage, such as swelling or loose connections.
- Propeller Inspection: Carefully examine each propeller for cracks, chips, or bends. Replace any damaged propellers.
- GPS Signal Acquisition: Ensure the drone has acquired a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This is essential for accurate positioning and safe autonomous flight modes.
- Gimbal and Camera Check: Check that the gimbal is functioning correctly and the camera is securely mounted. Test the camera functionality to ensure image quality.
- Flight Controller Check: Confirm that the flight controller is functioning properly and all sensors are calibrated.
- Visual Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the entire drone for any visible damage or loose components.
- Environment Check: Assess the surrounding environment for any potential hazards, such as obstacles, strong winds, or nearby power lines.
Drone Safety Feature Comparison
Different drones offer various safety features. Understanding these features is vital for making informed decisions and operating the drone safely.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obstacle Avoidance | Sensors detect obstacles and automatically adjust flight path. | Reduces collision risk, increases safety. | May not detect all obstacles, can be less effective in complex environments. |
| Emergency Stop | Allows immediate cessation of all motor functions. | Critical in emergency situations to prevent accidents. | Requires immediate reaction from the pilot. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | Drone automatically returns to its takeoff point. | Useful in case of signal loss or low battery. | Effectiveness depends on GPS signal strength and environmental conditions. |
| Geofencing | Limits the drone’s flight range to a predefined area. | Prevents accidental flyaways and ensures drone stays within safe boundaries. | Requires proper setup and configuration. |
Emergency Procedures
In the event of a drone malfunction or loss of signal, immediate action is crucial. The specific procedures will vary depending on the drone model, but generally include:
- Attempting to regain control using the available emergency functions (e.g., RTH).
- If regaining control is impossible, visually tracking the drone’s location to aid in recovery.
- Contacting local authorities if the drone poses a safety hazard.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls requires practice and understanding of the various flight modes and functionalities. Proper calibration is the first step towards safe and effective drone operation.
Drone Control Calibration

Calibrating the drone’s controls ensures accurate and responsive movements. The specific steps vary depending on the drone model, but generally involve:
- Powering on the drone and controller.
- Following the manufacturer’s instructions for calibrating the gyroscope and accelerometer.
- Performing a compass calibration, usually by rotating the drone in a figure-eight pattern.
- Testing the controls to ensure smooth and accurate movements in all directions.
Mastering Smooth Drone Movements
Smooth and controlled movements are key to achieving professional-looking aerial footage. This requires practice and patience. Start with slow, deliberate movements, gradually increasing speed and complexity as your skills improve.
- Use small, precise stick movements.
- Avoid abrupt changes in direction or altitude.
- Practice hovering in place before attempting more complex maneuvers.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and autonomy. Understanding these modes is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a constant altitude, allowing for horizontal movements without worrying about drifting up or down.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS signals for precise positioning and stability, enabling features like RTH.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): The drone automatically returns to its takeoff point, a crucial safety feature.
- Attitude Mode: The drone maintains its orientation relative to the pilot, even if the GPS signal is lost.
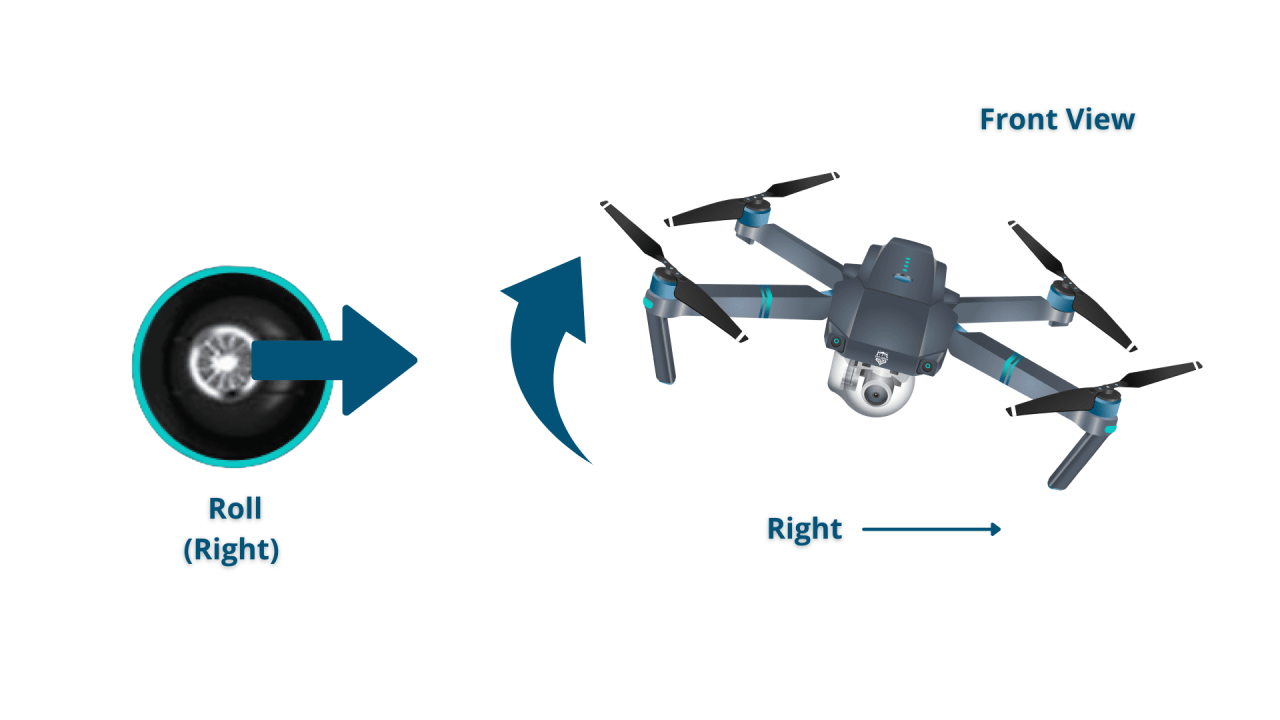
Drone Control Stick Layout
A typical drone controller has two joysticks. The left joystick controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick controls direction and speed.
Left Joystick:
Up: Ascend
Down: Descend
Left: Yaw Left
Right: Yaw Right
Right Joystick:
Forward: Move Forward
Backward: Move Backward
Left: Move Left
Right: Move Right
Taking Off, Landing, and Basic Maneuvers
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. Mastering these procedures minimizes the risk of accidents and damage.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
A safe takeoff and landing typically involves:
- Finding a clear, open area away from obstacles.
- Ensuring a strong GPS signal.
- Performing a pre-flight check.
- Slowly lifting off vertically.
- Maintaining a stable hover before making any movements.
- For landing, slowly descend vertically, maintaining a stable hover just above the ground before setting down gently.
Maintaining a Stable Hover
Hovering is a crucial skill that requires precise control of the drone’s movements. Practice hovering in a calm environment before attempting more complex maneuvers. Use small, incremental adjustments to maintain a stable position.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Once comfortable with hovering, practice basic maneuvers, including:
- Forward movement
- Backward movement
- Sideways movement (left and right)
- Rotational movement (yaw)
Common Takeoff and Landing Mistakes
Avoid these common mistakes to ensure safe and successful flights:
- Taking off in windy conditions.
- Failing to check battery level before takeoff.
- Ignoring pre-flight checks.
- Landing in uneven terrain.
- Not allowing enough space for takeoff and landing.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Advanced techniques allow for more creative and complex drone operations, opening up possibilities for professional-quality aerial photography and videography.
Waypoint Programming
Waypoints are pre-programmed points in space that the drone will automatically navigate to. This allows for complex, automated flight paths, useful for filming cinematic shots or surveying large areas. Most drone software provides tools to create and manage waypoints easily.
Filming Smooth Cinematic Shots

Achieving smooth cinematic shots requires careful planning and execution. Key elements include:
- Using slow, deliberate movements.
- Planning your shots beforehand.
- Experimenting with different camera angles and perspectives.
- Using features like “orbit” or “follow” modes.
Aerial Photography and Videography Tips
Capturing stunning aerial footage involves understanding composition, lighting, and camera settings. Consider the following:
- Rule of Thirds: Position key elements along imaginary lines dividing the frame into thirds.
- Leading Lines: Use natural lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the scene.
- Lighting: Avoid harsh midday sun; shoot during the golden hour for softer, more flattering light.
Drone Camera Settings Comparison
Understanding drone camera settings allows for fine-tuning image quality. Key settings include:
- ISO: Controls sensitivity to light (higher ISO = more noise).
- Shutter Speed: Controls exposure time (faster shutter speed = sharper images, less motion blur).
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens (wider aperture = shallower depth of field).
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation. This involves both routine checks and addressing any issues that may arise.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the drone and its components for any damage after each flight.
- Cleaning: Clean the drone body, propellers, and camera lens regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the drone’s firmware updated to benefit from bug fixes and new features.
- Calibration: Periodically recalibrate the drone’s sensors to maintain accuracy.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Some common drone problems and their potential solutions are:
- Low Battery: Charge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Recalibrate the gimbal or contact support.
Battery Care and Storage
Proper battery care is essential for maximizing battery lifespan and safety. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Avoid fully discharging or overcharging batteries.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A flowchart could visually represent troubleshooting steps, starting with identifying the problem and following a series of checks to isolate and resolve the issue. This would be a visual aid, not explicitly written here, but would involve boxes and arrows indicating decision points and actions.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to both legal regulations and ethical guidelines. Ignoring these aspects can lead to legal repercussions or social disapproval.
Local Drone Regulations, How to operate a drone
It is crucial to understand and comply with all local drone regulations. These regulations vary by country and region and often cover aspects such as registration, flight restrictions, and airspace limitations. Always check with the relevant authorities before flying.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical drone operation involves respecting the privacy of others and avoiding any actions that could be considered intrusive or harmful. This includes avoiding filming people without their consent and respecting private property.
Restricted and Prohibited Areas
Drone operation is often restricted or prohibited in certain areas, such as airports, military bases, and sensitive infrastructure. Always check for any flight restrictions before flying.
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation includes:
- Respecting privacy and avoiding filming people without their consent.
- Staying aware of your surroundings and avoiding obstacles.
- Flying only in safe and legal areas.
- Keeping the drone within visual line of sight.
- Being mindful of noise levels.
Drone Photography and Videography Composition
Drone photography and videography offers unique perspectives and creative possibilities. Mastering composition techniques elevates your aerial footage from snapshots to stunning visuals.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation.
Camera Angles and Shots
- High-Angle Shot: Looking down on the subject from above.
- Low-Angle Shot: Looking up at the subject from below.
- Overhead Shot: Directly above the subject.
- Tracking Shot: Following a moving subject.
- Orbit Shot: Circling around a subject.
Framing Shots Effectively
Effective framing involves considering the subject, background, and overall composition. For landscapes, use wide shots to capture the grandeur. For portraits, focus on the subject and use shallow depth of field. For action shots, capture movement and energy.
Capturing Stunning Aerial Footage
To capture stunning aerial footage, consider the following:
- Golden Hour Lighting: Shoot during sunrise or sunset for soft, warm light.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques.
- Movement: Use smooth, deliberate movements to avoid jerky footage.
Drone Camera Settings
Understanding the effects of different camera settings is crucial for achieving desired image quality. Key settings and their effects include:
- ISO: Higher ISO values increase sensitivity to light, but also increase noise.
- Shutter Speed: Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: A wider aperture (smaller f-number) creates a shallower depth of field, blurring the background.
- White Balance: Adjusts the color temperature to accurately represent colors.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding experience, combining technology, skill, and creativity. From the initial thrill of takeoff to the satisfaction of capturing breathtaking footage, this journey empowers you to explore new perspectives and document the world from above. Remember, responsible operation and adherence to regulations are paramount. With practice and a commitment to safety, you can confidently navigate the skies and unlock the full potential of your drone.
Commonly Asked Questions: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Mastering the techniques outlined will enable you to confidently and safely operate your drone, ensuring both successful flights and responsible drone usage.
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Look for models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, though larger drones can offer longer flight times.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically bring the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. Check your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
Is drone insurance necessary?
Drone insurance is highly recommended to cover potential damage or injury caused by accidents. Check your local regulations as insurance requirements can vary.